Freedom of speech, a cornerstone of democratic societies, is the right to express opinions without censorship, restraint, or legal penalty. It encompasses not only the spoken and written word but also all forms of communication, from art to protests, and digital media. This fundamental right is essential for individual autonomy, the pursuit of truth, and the functioning of a healthy democracy.
The concept of freedom of speech has evolved significantly over the centuries. Rooted in ancient Greek philosophy, it gained prominence during the Enlightenment, shaping modern democratic ideals. Philosophers like John Milton and John Stuart Mill argued for the importance of free expression as a means to discover the truth and promote societal progress. The 18th and 19th centuries saw these ideas crystallize into legal protections, notably in the United States Bill of Rights and the French Declaration of the Rights of Man and the Citizen.
In today’s interconnected world, freedom of speech has taken on new dimensions. The advent of the internet and social media has revolutionized how we communicate, offering unprecedented platforms for expression. This digital era has democratized information dissemination, enabling anyone with internet access to share their views with a global audience. However, it also presents new challenges, such as the spread of misinformation, hate speech, and the role of tech giants in regulating online content.
The Essence of Freedom of Speech
At its core, freedom of speech is about the right to challenge, question, and change the world around us. It is the bedrock of democratic engagement, allowing for the exchange of diverse ideas and opinions. This freedom is not just about the ability to speak but also the right to listen, to be heard, and to participate in the public discourse that shapes our societies.
As we navigate the complexities of the 21st century, the importance of freedom of speech remains undiminished. It is a tool for social change, a defense against tyranny, and a means to hold those in power accountable. Upholding and protecting this right is crucial for the continued advancement and enrichment of our global community.
Historical Evolution of Freedom of Speech

The concept of freedom of speech traces its roots back to ancient civilizations. In classical Athens, the notion of ‘parrhesia’ – speaking candidly without fear of retribution – was a valued part of public discourse, particularly in the context of the Athenian democracy. However, this freedom was not absolute and was often a privilege rather than a right, limited to certain classes of people.
Influence of Enlightenment Thinkers
The Enlightenment era marked a significant turning point in the evolution of freedom of speech. Philosophers like John Locke, Voltaire, and Baruch Spinoza championed the idea of free expression as a natural right. Locke’s theories on individual liberty and the social contract laid the groundwork for modern democratic thought. Voltaire’s fierce defense of free speech, encapsulated in his famous quote, “I disapprove of what you say, but I will defend to the death your right to say it,” highlighted the importance of tolerance and open debate.
Codification in Law and the Birth of Modern Democracies
The Enlightenment ideas were instrumental in shaping the legal frameworks of emerging democracies. The United States Constitution’s First Amendment (1791) and the French Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen (1789) were among the first legal documents to secure freedom of speech as a fundamental right. These documents marked a paradigm shift from the notion of free speech as a privilege to a universally recognized right.
19th and 20th Century Developments
Throughout the 19th and 20th centuries, the scope and understanding of freedom of speech continued to evolve. In the United States, landmark Supreme Court cases like Schenck v. United States (1919) and Brandenburg v. Ohio (1969) refined the legal boundaries of free speech, introducing concepts like “clear and present danger” and “imminent lawless action” as limits to this right. In Europe, the aftermath of World War II and the horrors of totalitarian regimes led to a renewed emphasis on human rights, culminating in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights in 1948, which recognized freedom of opinion and expression as fundamental human rights.
Global Expansion and Challenges
In the latter half of the 20th century, many countries around the world began to adopt similar protections for freedom of speech, often as part of broader movements toward democratization. However, the extent and interpretation of this right varied significantly, influenced by cultural, political, and social factors. In many parts of the world, the struggle for free expression remained fraught with challenges, including censorship, repression, and the persecution of dissenting voices.
The historical evolution of freedom of speech is a testament to its enduring importance in human society. From its philosophical origins in ancient Greece to its codification in modern democracies, this right has been central to the development of free, open, and progressive societies. As we move forward, understanding this history is crucial in addressing the contemporary challenges and ensuring that the spirit of free expression continues to thrive.
Legal Framework and Global Perspectives

The post-World War II era marked a significant milestone in the legal recognition of freedom of speech as a global human right. The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR), adopted by the United Nations in 1948, was a landmark document in this regard. Article 19 of the UDHR explicitly states that everyone has the right to freedom of opinion and expression. This right includes the freedom to hold opinions without interference and to seek, receive, and impart information and ideas through any media, regardless of frontiers. Subsequent international treaties, like the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR), further cemented this right in international law.
Diverse Legal Landscapes Across Countries
Despite the universal recognition of freedom of speech in international law, its implementation varies significantly across different nations. In the United States, the First Amendment offers robust protection of free speech, making it one of the most speech-protective countries in the world. European countries, while also valuing free expression, often impose more restrictions, particularly around hate speech and Holocaust denial, reflecting their historical contexts.
In contrast, many authoritarian regimes severely restrict freedom of speech, using laws against defamation, sedition, or blasphemy to stifle dissent and control public discourse. Countries like China and North Korea are known for their stringent control over media and the internet, often justifying censorship in the name of social stability and national security.
Notable Legal Cases Shaping Free Speech
Several landmark legal cases have shaped the current understanding of freedom of speech. In the United States, cases like New York Times Co. v. Sullivan (1964) revolutionized libel law, protecting media rights to criticize public officials. In Europe, the European Court of Human Rights has dealt with numerous cases balancing free speech with privacy and reputation, such as the Handyside v. United Kingdom (1976).
The legal framework surrounding freedom of speech is as diverse as the world’s cultures and political systems. While international law sets a standard, national laws and court decisions reflect the unique historical, cultural, and political contexts of each country. Understanding these differences is crucial in appreciating the global landscape of free expression and the ongoing efforts to protect this fundamental right in various societies.
Freedom of Speech in the Digital Age

The advent of the internet and social media has revolutionized the landscape of freedom of speech. This digital age has democratized the flow of information, enabling individuals to share their views and access a wealth of knowledge with unprecedented ease. The internet has emerged as a powerful platform for free expression, activism, and the dissemination of ideas across global boundaries.
Challenges Posed by Digital Platforms
However, this digital freedom comes with significant challenges. The vast reach and anonymity of the internet can lead to the spread of misinformation, hate speech, and extremist content. Social media platforms, while facilitating free expression, also grapple with the need to moderate content to prevent harm. This has led to complex debates about the role of these platforms in regulating speech and the fine line between censorship and responsible moderation.
The issue of “echo chambers” and “filter bubbles” – where users are exposed only to information that aligns with their existing beliefs – has also raised concerns about the quality of public discourse in the digital realm. These phenomena can lead to polarization and reduce the opportunity for healthy, diverse dialogues.
Recent Developments and Landmark Decisions
Governments and international bodies have begun to respond to these challenges. The European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Digital Services Act are examples of efforts to regulate digital platforms and protect users’ rights online. In the United States, debates around Section 230 of the Communications Decency Act, which provides immunity to online platforms from liability for user-generated content, highlight the ongoing struggle to balance free speech with accountability.
Legal cases like Google Spain SL, Google Inc. v. Agencia Española de Protección de Datos, Mario Costeja González (2014), which led to the “right to be forgotten” in the EU, illustrate the complex interplay between freedom of speech, privacy, and the digital world.
The digital age has transformed the way we understand and exercise freedom of speech. While it offers unparalleled opportunities for free expression, it also presents new challenges that require careful navigation. Balancing the right to free speech with the need for responsible communication in the digital era is one of the key challenges of our time, necessitating ongoing dialogue and adaptive legal frameworks.
Contemporary Challenges and Debates
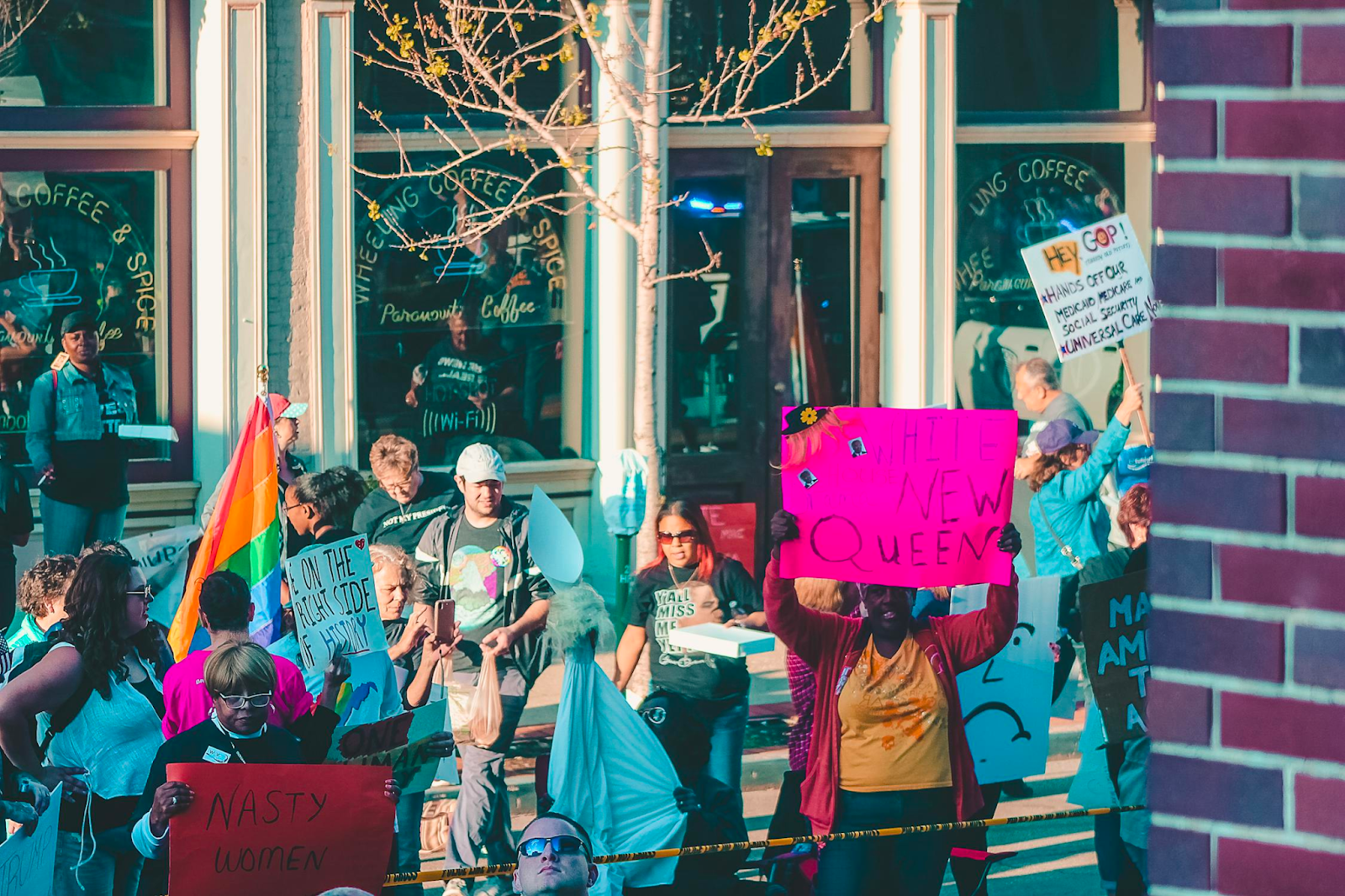
In the modern context, freedom of speech often finds itself at a crossroads with other fundamental rights. The challenge lies in balancing this freedom with the right to privacy, protection from hate speech, and the prevention of misinformation. Democracies worldwide grapple with questions about where to draw the line: How much regulation is too much? What constitutes harmful speech? These questions become even more complex with the rise of digital platforms, where the speed and reach of communication amplify the impact of these issues.
Government and Corporate Regulation of Speech
Another significant debate centers around the role of governments and corporations in regulating speech. Governments are tasked with protecting freedom of speech while also safeguarding citizens from harmful content. This dual responsibility can lead to controversial decisions, such as imposing regulations on media houses or internet censorship under the guise of national security. Similarly, tech giants like Facebook, X (Twitter), and Google wield significant power over public discourse. Their policies on content moderation and algorithmic curation have profound implications for free speech and the diversity of viewpoints in the digital public square.
Notable Controversies and Public Opinion
Recent years have seen several high-profile controversies that highlight the complexities of free speech in today’s world. The deplatforming of public figures, the debate over “cancel culture,” and the spread of fake news and conspiracy theories are just a few examples. These incidents spark widespread public debate and reflect the evolving nature of free speech. They also raise questions about the responsibilities of individuals and institutions in upholding the principles of open and respectful discourse.
The contemporary challenges and debates surrounding freedom of speech are indicative of its dynamic nature in a rapidly changing world. As societies evolve, so do the interpretations and implications of this fundamental right. Navigating these complexities requires a nuanced understanding of the interplay between free speech, technology, and societal norms, ensuring that this cherished freedom is preserved while adapting to new realities.
The Importance of Freedom of Speech Today

In today’s world, the importance of freedom of speech cannot be overstated. It is a cornerstone of democratic societies, facilitating open and transparent governance. By allowing for the free exchange of ideas and opinions, freedom of speech ensures that governments remain accountable and responsive to their citizens. It empowers individuals to challenge injustice, advocate for change, and contribute to the collective decision-making process.
Tool for Social Change and Awareness
Freedom of speech also serves as a powerful tool for social change. It enables marginalized voices to be heard, fostering a more inclusive and equitable society. Through various mediums – be it journalism, social media, or public protests – individuals and groups can raise awareness about critical issues, mobilize support, and drive societal progress. The recent global movements for racial justice and environmental action underscore the transformative power of free expression.
In an era marked by rapid technological advancements and complex social challenges, safeguarding freedom of speech is more crucial than ever. It is not just a right to be protected, but a principle to be actively upheld and promoted. As we navigate the uncertainties of the 21st century, the continued importance of freedom of speech in fostering informed, resilient, and progressive communities remains clear.
Conclusion: Freedom of Speech
The exploration of freedom of speech from its historical roots to its contemporary challenges underscores its enduring significance. This fundamental right, pivotal in shaping democratic societies, continues to evolve in the face of new technological and social landscapes. As we witness the ongoing debates and legal developments surrounding free speech, it’s clear that this liberty remains a vital component of a healthy, dynamic society. Upholding and adapting the principles of free expression to modern challenges is not just a legal imperative but a moral one, ensuring that the voices of all individuals can contribute to the collective narrative of our time.
Support the vital cause of protecting and promoting freedom of speech by donating to the First Freedoms Foundation, where your contribution can make a real difference in upholding this fundamental right.
Further Reading
For those interested in delving deeper into the topic of freedom of speech and its various facets, the following resources offer valuable insights and perspectives:
-
- “Free Speech: Ten Principles for a Connected World” by Timothy Garton Ash
An exploration of free speech in the digital age, examining the balance between liberty and security. Available here.
-
- “The First Amendment and the Fourth Estate: The Law of Mass Media” by T. Barton Carter, Marc A. Franklin, and Jay B. Wright
A comprehensive text on media law, offering an in-depth look at the legal aspects of freedom of speech. Available here.
-
- “The Silencing: How the Left is Killing Free Speech” by Kirsten Powers
An examination of how free speech is being undermined in modern American culture and politics. Available here.

